Torque = r F sinΘ
Learning Objectives
1. Be able to define and use the equation for torque.
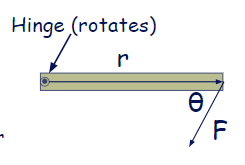
Torque is what causes an object to start twisting or rotating. Torque equals the
\( \tau=rFsin \theta\)
- r = moment arm or the distance from the pivot point to the force (m)
- F = Force (N)
- \( \theta\) = the angle between the force and the moment arm
Sample Problem
A crane lifts a load. If the mass of the load is 5000 kg, and the crane’s 22-m long arm is at a 75o angle relative to the horizontal, calculate the torque exerted about the point of rotation at the base of the crane arm. This is intended something of a trick problem so think carefully and check your answer with the video solution.

Torque From The Force of Gravity
If a rigid body has a fixed point of rotation that is not at its center of gravity then the force of gravity on the object exerts a torque. The force of gravity for the whole object acts at its center of mass.
Sample Problem
A 10kg, 4m long rigid bar of uniform density sits on a fulcrum placed 1.2m from the right edge of the bar. What is the torque acting on the bar?
Solution
Drawing a picture and include important measurements, and forces.
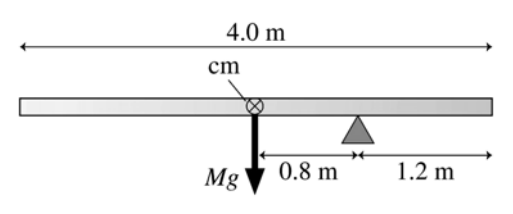
We place the weight of the bar at the center of mass. In this case that is 100N. We can see from our picture that the center of the bar is going to be .8m from the fulcrum or point of rotation.
\( \displaystyle \tau = rFsin\theta \; \tau =( .8m)(100N)(sin(90)=80Nm\)
